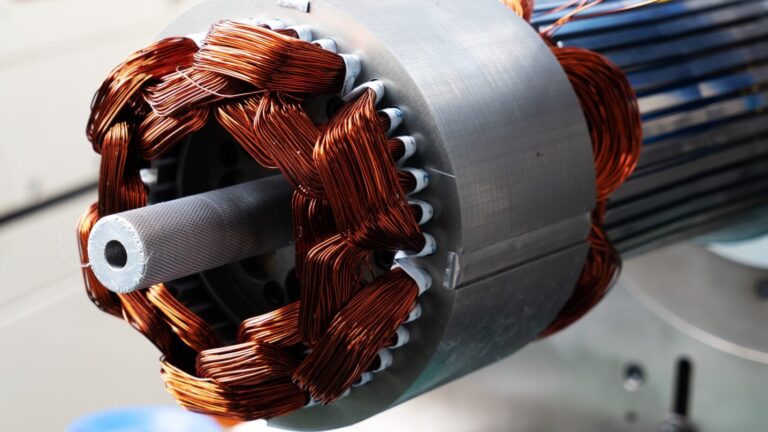
In the realm of electric motors, there are several critical components that work together to ensure efficient and reliable performance. One such component, often overlooked yet incredibly essential, is the humble grounding brush. Grounding brushes play a vital role in maintaining the safety and efficiency of electric motors, particularly in high-voltage and high-current applications. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of grounding brushes, exploring their history, construction, types, applications, and importance in electric motor operation.
A Brief History of Grounding Brushes
The concept of grounding brushes dates back to the early days of electric motor development. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, inventors like Nikola Tesla and George Westinghouse experimented with various materials and designs to create reliable and efficient electric motors. As motor designs evolved, the need for effective grounding mechanisms became apparent. The first grounding brushes were likely made from carbon or graphite, materials that provided a reliable path to ground for the motor’s electrical current.
Construction and Composition of Grounding Brushes
Grounding brushes are typically composed of a combination of materials, including:
1. Conductive Material
The primary component of a grounding brush, the conductive material provides a path for electrical current to flow to ground. Common materials used include carbon, graphite, copper, and silver.
2. Binder Material
A binding agent, such as a resin or polymer, holds the conductive material together, giving the brush its structural integrity.
3. Holding Mechanism
A spring, clip, or other retaining device holds the brush in place, ensuring consistent contact with the motor’s ground plane or bearing.
Types of Grounding Brushes
Grounding brushes come in various shapes, sizes, and configurations to cater to different motor designs and applications. Some common types of grounding brushes include:
1. Radial Brushes
Used in smaller motors, radial brushes have a circular shape and make contact with the ground plane at a 90-degree angle.
2. Axial Brushes
Larger motors often employ axial brushes, which make contact with the ground plane parallel to the motor’s axis.
3. Segmented Brushes
Segmented brushes consist of multiple smaller brushes arranged around the motor’s ground plane, providing improved current distribution and reduced wear.
4. Spring-Loaded Brushes
Spring-loaded brushes use a spring or other mechanism to maintain consistent contact with the ground plane, even in the presence of vibration or movement.
Applications of Grounding Brushes
Grounding brushes are essential components in a wide range of electric motors, including:
1. High-Voltage Motors
High-voltage motors, such as those used in industrial applications, rely on grounding brushes to ensure the safe and efficient transfer of electrical energy.
2. High-Current Motors
Motors that operate at high current levels, such as those used in heavy industries or transportation, require grounding brushes to prevent overheating and electrical arcing.
3. Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) Motors
VFD motors, which operate at varying frequencies and voltages, often employ grounding brushes to mitigate the effects of electrical noise and harmonics.
4. Explosion-Proof Motors
Explosion-proof motors, designed for use in hazardous environments, rely on grounding brushes to prevent electrical sparks and ensure safe operation.
Importance of Grounding Brushes in Electric Motor Operation
Grounding brushes play a vital role in maintaining the safety, efficiency, and reliability of electric motors. Some key aspects of their importance include:
1. Electrical Safety
Grounding brushes provide a safe path to ground for electrical current, preventing the risk of electrical shock or arcing.
2. Efficient Energy Transfer
Grounding brushes ensure efficient energy transfer between the motor’s windings and the ground plane, reducing energy losses and heat generation.
3. Motor Protection
Grounding brushes help protect the motor from overvoltage, overcurrent, and electrical surges, which can cause damage or failure.
4. Reducing Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
Grounding brushes can help reduce EMI, which can interfere with surrounding electronics and communication systems.
Challenges and Limitations of Grounding Brushes
While grounding brushes are an essential component of electric motors, they are not without their challenges and limitations. Some common issues associated with grounding brushes include:
1. Wear and Tear
Grounding brushes can wear down over time, requiring regular inspection and replacement to maintain motor performance and safety.
2. Electrical Noise
Grounding brushes can generate electrical noise, which can interfere with surrounding electronics and communication systems.
3. Heat Generation
High-friction or poorly designed grounding brushes can generate excessive heat, reducing motor efficiency and lifespan.
4. Material Degradation
Grounding brushes can degrade over time, losing their electrical conductivity and wear resistance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, grounding brushes are a critical yet often overlooked component of electric motors. Their unique properties and construction make them an ideal solution for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electric motors, particularly in high-voltage and high-current applications. By understanding the history, types, applications, and importance of grounding brushes, we can better appreciate the intricate design and operation of electric motors.
As the demand for efficient and sustainable technologies continues to grow, the importance of grounding brushes in electric motor design will only continue to increase. By pushing the boundaries of grounding brush technology and exploring new materials and designs, we can unlock even greater efficiencies and performance in the electric motors of the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average lifespan of a grounding brush?
The average lifespan of a grounding brush varies depending on the motor design, operating conditions, and quality of the brush. Typically, grounding brushes can last anywhere from a few hundred to several thousand hours.
How often should I inspect and replace my grounding brushes?
Regular inspection and replacement of grounding brushes are crucial to maintaining motor performance and safety. The recommended inspection and replacement schedule varies depending on the motor type and application.
Can I use grounding brushes in high-temperature applications?
While grounding brushes can operate in high-temperature environments, their performance and lifespan may be compromised. Specialized high-temperature brushes made from materials like ceramic or advanced polymers are available for such applications.
Are grounding brushes compatible with all motor types?
Grounding brushes are used in a wide range of electric motors, including DC, universal, AC, and stepper motors. However, certain motor designs, such as brushless motors, do not require grounding brushes.
What are the benefits of using silver or copper grounding brushes?
Silver and copper grounding brushes offer improved electrical conductivity and reduced wear rates compared to carbon or graphite brushes. They are often used in high-performance or high-reliability applications.